Porous Annular Gap Grout in Shield Tunnelling
Test Procedures for the Assessment of Durability under Sulphate ExposureUntil now, segment-lined tunnels in low mountain formations have been constructed with one layer of pressure-tight lining, with sealing being provided by elastomer gasket profiles. The application limit of this method of construction is about 5 bar. If the water pressure is higher, a much more elaborate and thus more expensive double-shell construction with an additional drainage layer between the inner and outer lining is necessary. In the recent past, a solution for this problem in mechanised tunnelling with segment lining has often been discussed in the specialist world: a drainage layer of permeable material for annular gap grouting. This would then make the installation of an additional inner lining with drainage layer no longer necessary.
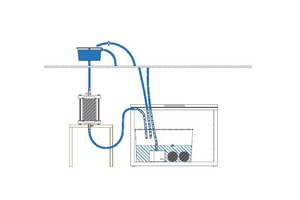
The current article presents the results and conclusions regarding investigations of the durability of a cement-based, porous annular gap filling material, which were part of a master thesis at the Institute for Tunnelling and Construction Management at the Ruhr University Bochum, Germany. For the presented tests, cylindrical, porous test volumes (d= 10 cm, l = 30 cm) were made from cement paste and tested after hardening.
As a conclusion, it can already be stated in advance that the existing test procedures are not suitable for the assessment of durability. In addition, further adaptations to...